Building Efficiency & Resilience for Your Long-Term Energy Needs
The demands on our nation’s electrical grid grow and evolve with each passing year, leaving industry leaders with the challenge of adapting our current grid infrastructure to increase reliability, efficiency, and long-term resilience. Distributed energy resources (DERs) have proven to be an essential strategy in achieving these aims, providing business owners and leaders with alternative energy supplies to help prepare today’s organizations for the changing future. These resources are accessible, customizable, and can boost energy efficiency while reducing long-term energy costs. Let’s dive into how the technology works and discover ways it can impact your organization’s energy goals.
What is Distributed Energy?
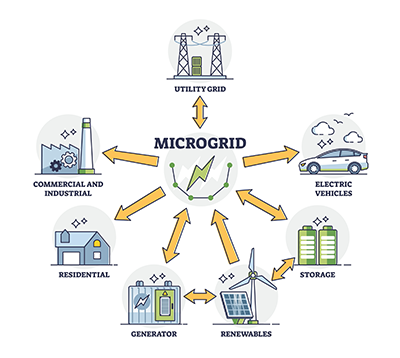
Distributed energy utilizes small-scale energy generation devices to deliver power directly to a facility, industrial campus, or even a small community. Examples of DERs include:
- Battery Storage Systems
- Fuel Cells
- Rooftop Solar
- Large Scale Solar Panel Power Systems
- Wind Turbines
- Hydropower
- Generators
DERs produce energy on-site, delivering power directly to the end consumer and then feeding any excess energy back into the main electrical grid. Since each DER is capable of differing electrical outputs, custom systems can be built to meet an individual facility’s unique energy demands. Small and medium-sized businesses can use DERs as their primary power source, only relying on the centralized power grid as a backup. Typically, DERs are privately owned and operated, but regional networks of individual DERs can sometimes be managed by municipal power authorities.
In contrast to DERs, centralized, large-scale power plants (such as coal or nuclear) are typically located far away from population centers and require a network of transmission lines to power the larger electrical grid. While these larger power plants have been effective in reaching rural communities and powering dense urban settings, they are expensive to operate and prone to outages, especially as the demand for higher energy outputs grows with evolving technologies.
What Are the Benefits of Distributed Energy?
Efficiency
A DER provides energy directly to an end-consumer, meaning that it does not have to travel from a centralized power plant through transmission lines. This reduces energy loss and increases overall energy efficiency.
Cost
DER users also benefit from lower energy costs. Operating a privately owned power source protects your organization from rising energy costs from a regional power supplier, even if you aren’t able to get 100% of your electricity from the DER. In addition, you can be reimbursed for any excess energy that your DER puts back into the regional electrical grid.
Resilience
Power source diversification provides an added layer of protection for unexpected curve balls. If a centralized grid faces a critical outage or extreme weather decreases solar or wind energy output, having diverse power sources can keep your organization up and running.
Renewable Energy
While not all DERs are considered renewable energy sources, they tend to rely on renewable sources. Utilizing DERs allows businesses and organizations to do their part in reducing overall carbon emissions and improving local sustainability.
Leveraging DERs For Your Organization
RedHawk Energy has decades of experience with renewable energy and is poised to provide distributed energy resources to our clients in the rail, telecommunications, public infrastructure, and industrial sectors. From education on applicable technologies to feasibility studies to on-site technical support, our team can help your organization make the most of this technology. Contact our team to learn more.